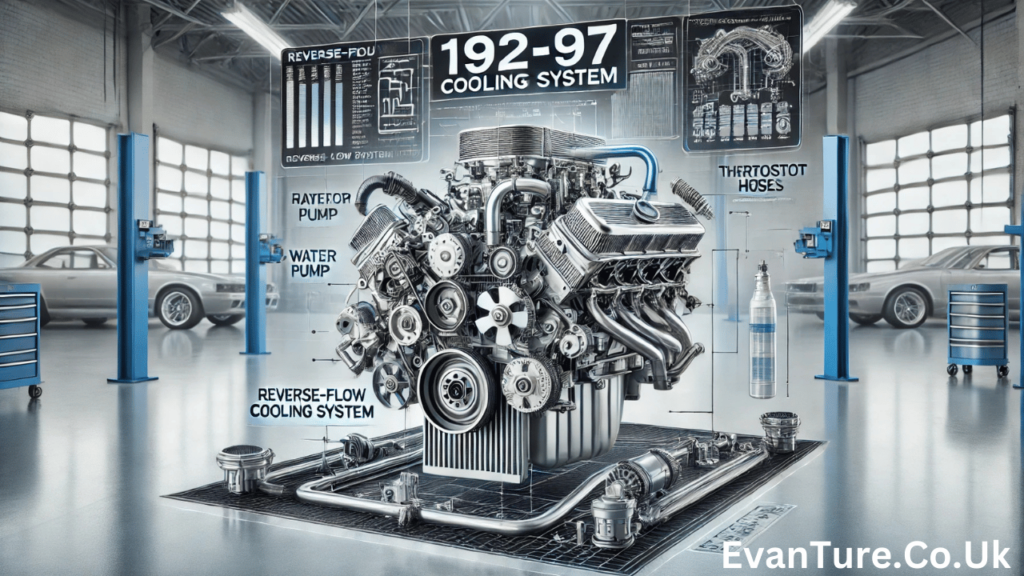
The 192-97 LT1 cooling system is a hallmark of General Motors’ engineering innovation, designed to maximize the performance and longevity of the LT1 engine series. This advanced cooling system played a pivotal role in enhancing the engine efficiency by employing unique features like reverse-flow cooling. Understanding its components, functionality, and maintenance requirements is crucial for car enthusiasts and owners of vehicles equipped with this engine. In this article, we will delve deep into the 192-97 LT1 cooling system, exploring its design, common issues, and practical maintenance tips to ensure optimal performance.
What Makes the 192-97 LT1 Cooling System Unique?
The 192-97 LT1 cooling system stands out primarily because of its reverse-flow design. Unlike traditional systems that cool the engine block first and then the cylinder heads, this system reverses the process. By cooling the cylinder heads first, it enables the engine to operate at higher compression ratios without the risk of detonation. This design enhances both performance and fuel efficiency.
Key Benefits of Reverse-Flow Cooling
- Improved Efficiency: Cooling the heads first maintains a more consistent temperature, reducing the risk of hotspots.
- Enhanced Power Output: The system supports higher compression ratios, which translates to better power delivery.
- Reduced Engine Wear: Consistent cooling minimizes thermal stress on engine components.
Key Components of the 192-97 LT1 Cooling System
To appreciate the complexity and efficiency of the 192-97 LT1 cooling system, it essential to understand its primary components and their functions:
Radiator
The radiator serves as the central hub for heat dissipation. It designed with a network of tubes and fins that allow coolant to release heat effectively before recirculating through the engine.
Water Pump
The water pump is the powerhouse of the cooling system, ensuring consistent coolant circulation. Driven by the serpentine belt, it pushes coolant through the engine, radiator, and back.
Thermostat
This critical component regulates the flow of coolant based on engine temperature. It opens to allow hot coolant into the radiator and closes to maintain optimal engine temperature during cold starts.
Hoses and Connections
Rubber hoses transport coolant between various components. Their integrity is vital to prevent leaks and ensure efficient circulation.
Coolant Reservoir
The reservoir stores excess coolant and accommodates expansion as the engine heats up. It also serves as a visual indicator for coolant levels.
Common Issues with the 192-97 LT1 Cooling System
Despite its advanced design, the 192-97 LT1 cooling system is not without its challenges. Regular maintenance and early detection of issues are crucial to prevent severe engine damage.
Overheating Problems
Overheating is one of the most common issues. This can result from several factors:
- Faulty thermostat
- Failing water pump
- Clogged radiator
Coolant Leaks
Leaks often occur in hoses, the radiator, or the water pump. These can lead to a loss of coolant and reduced efficiency.
Clogged Radiator
Debris and sediment can accumulate in the radiator over time, restricting coolant flow and reducing heat dissipation.
Water Pump Failure
Symptoms of a failing water pump include coolant leaks near the pump, unusual noises, and fluctuating temperature readings.
Thermostat Malfunction
A thermostat stuck in the open or closed position can lead to either overheating or underheating, affecting engine performance.
Maintenance Tips for the 192-97 LT1 Cooling System
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the 192-97 LT1 cooling system. Here are some practical tips:
Regular Coolant Changes
Changing the coolant every two to three years prevents corrosion and buildup of debris. Always use the manufacturer-recommended coolant type.
Inspect and Replace Hoses
Check hoses for cracks, bulges, or leaks. Replace damaged hoses promptly to prevent coolant loss.
Flush the Radiator
Periodically flushing the radiator removes sediment and debris, ensuring optimal coolant flow and heat dissipation.
Monitor Coolant Levels
Regularly check the coolant reservoir to ensure levels are within the recommended range. Low coolant can lead to overheating.
Test the Thermostat
Inspect the thermostat periodically to ensure it opens and closes correctly. Replace it if it shows signs of malfunction.
Check the Water Pump
Listen for unusual noises and inspect the area around the pump for leaks. Replace the pump if it shows signs of wear or failure.
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues
Overheating
If the engine overheats, start by inspecting the thermostat, water pump, and radiator for any signs of malfunction. Replacing the faulty component is often the solution.
Coolant Leaks
Identify the source of the leak by inspecting hoses, connections, and the radiator. Tighten loose connections or replace damaged parts as needed.
Clogged Radiator
A clogged radiator may require professional cleaning or replacement. Ensure you flush the cooling system regularly to avoid this issue.
Thermostat Problems
A simple thermostat test can confirm whether it functioning correctly. If not, replace it with a new one.
Water Pump Issues
Inspect the water pump for leaks or noises. A failing water pump should be replaced immediately to prevent engine damage.
Why Regular Maintenance is Essential
Neglecting the 192-97 LT1 cooling system can lead to severe engine damage and costly repairs. Regular inspections, timely replacements, and using high-quality components are essential to keep the system running smoothly.
By staying proactive, you can ensure the longevity of your engine and enjoy optimal performance for years to come. Maintaining the cooling system is not just about avoiding breakdowns but also about preserving the value and reliability of your vehicle.
FAQs about the 192-97 LT1 Cooling System
1. What is the purpose of the reverse-flow cooling design in the 192-97 LT1 cooling system? The reverse-flow design cools the cylinder heads first, allowing for higher compression ratios and improved engine efficiency.
2. How often should I change the coolant in the 192-97 LT1 cooling system? It recommended to change the coolant every two to three years to prevent corrosion and maintain optimal performance.
3. What are common signs of a failing water pump in the 192-97 LT1 cooling system? Common signs include coolant leaks near the pump, unusual noises, and fluctuating engine temperatures.
4. How can I prevent radiator clogs in the 192-97 LT1 cooling system? Regularly flush the radiator and use high-quality coolant to prevent debris and sediment buildup.
5. What should I do if my engine overheats despite regular maintenance? Check the thermostat, radiator, and water pump for issues. If the problem persists, consult a professional mechanic for a thorough inspection.
Conclusion
The 192-97 LT1 cooling system exemplifies engineering innovation, combining efficiency and performance through its unique reverse-flow design. By understanding its components, addressing common issues, and adhering to regular maintenance practices, owners can ensure the system reliability and longevity. Whether you’re tackling overheating problems or performing routine checks, proactive care for the 192-97 LT1 cooling system will keep your engine running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
Read More: Understanding the can i buy 1.5f8-p1uzt Texture: A Comprehensive Guide